Recompilare OpenSSL 1.1 & Ningin 1.25 para TLS 1.3 (Centos 7)

recompilar OpenSSL 1.1 & NGINX 1.25 para TLS 1.3 (CentOS 7), siguiendo el escenario donde ya lo ha instalado en el servidor o versión anterior openssl asociado con el servicio nginx.
contenido
Más concretamente, para poder activar OpenSSL 1.1.1t por el servicio NGINX, que se ejecuta con una versión anterior. OpenSSL 1.0.2k.
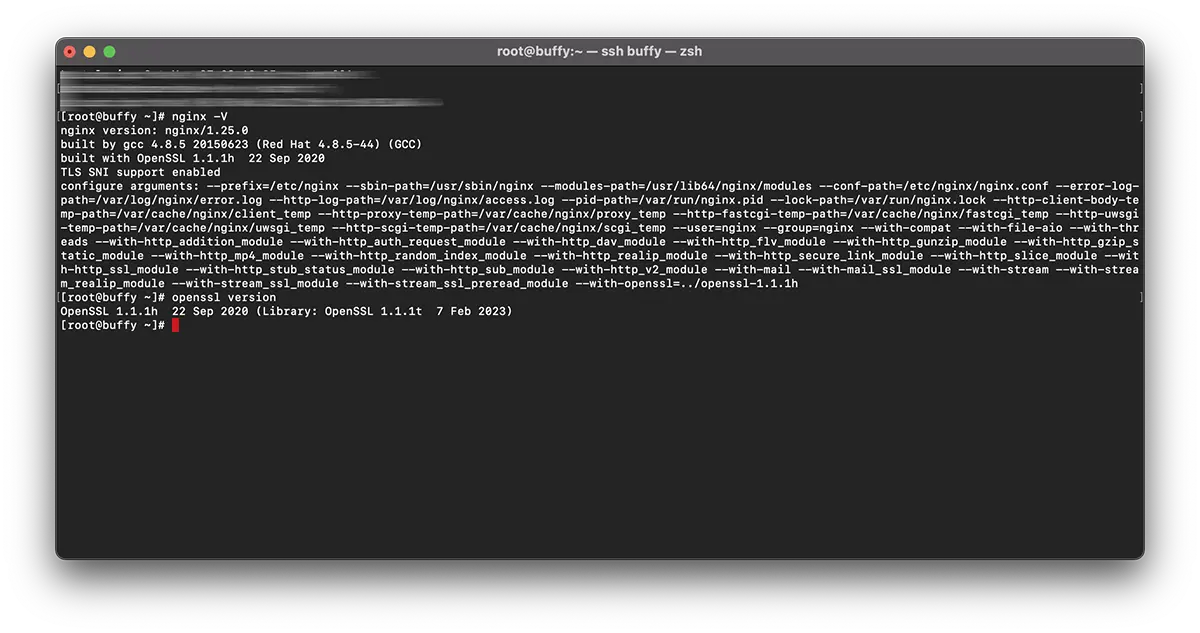
# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.25.0
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
TLS SNI support enabled# openssl version -a
OpenSSL 1.1.1t 7 Feb 2023Esto significa que existen dos versiones diferentes de OpenSSL. Una versión instalada en el sistema a través de “yum” (1.0.2k-fips) y una versión OpenSSL instalado por compilación manual (openssl 1.1.1t).
Clásicamente, la mayoría recomienda reinstalar ‘OpenSSL‘ a nivel de servidor. Esto implicaría ejecutar el comando: yum remove openssl. Pero aquí hay un gran problema. Con la desinstalación de la versión antigua. OpenSSL, es posible que también necesites desinstalar algunas aplicaciones dependientes. Como: nginx, MariaDB-server, cerbot, y muchos más.
- ¿Cómo se activa TLSV1.3 en Ninx? Vestacp / Centos o Ubuntu
- Período de validez máxima TLS / SSL certificado en 2023
- Las diferencias entre TLS 1.2 y TLS 1.3 – Velocidad y seguridad
Una solución más sencilla es recompilar openssl 1.1 & nginx 1.25 para TLS 1.3.
Tutorial recompilar OpenSSL 1.1 & NGINX 1.25 para TLS 1.3 (CentOS 7)
En mi ejemplo, la recopilación es para nginx/1.25.0 & OpenSSL 1.1.1h usando librerías OpenSSL 1.1.1t.
Recompilar NGINX.
1. Cree el archivo: nginx-with-tls13-compile.sh
sudo nano nginx-with-tls13-compile.shdonde agregas el script:
#!/bin/bash
## nginx
NGINX=nginx-1.25.0.tar.gz
if [ ! -f "${NGINX}" ];then
wget https://nginx.org/download/${NGINX}
fi
ND=$(basename $NGINX .tar.gz)
if [ ! -d "${ND}" ];then
tar zxvf ${NGINX}
fi
cd ${ND}
## pre require package
## yum install gcc pcre-devel zlib-devel
./configure --prefix=/etc/nginx \
--sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx \
--modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules \
--conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf \
--error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log \
--http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \
--pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid \
--lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock \
--http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_temp \
--http-proxy-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp \
--http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp \
--http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp \
--http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp \
--user=nginx \
--group=nginx \
--with-compat \
--with-file-aio \
--with-threads \
--with-http_addition_module \
--with-http_auth_request_module \
--with-http_dav_module \
--with-http_flv_module \
--with-http_gunzip_module \
--with-http_gzip_static_module \
--with-http_mp4_module \
--with-http_random_index_module \
--with-http_realip_module \
--with-http_secure_link_module \
--with-http_slice_module \
--with-http_ssl_module \
--with-http_stub_status_module \
--with-http_sub_module \
--with-http_v2_module \
--with-mail \
--with-mail_ssl_module \
--with-stream \
--with-stream_realip_module \
--with-stream_ssl_module \
--with-stream_ssl_preread_module \
--with-openssl=../$(basename $OPENSSL .tar.gz)
make
sudo make install
nginx -VGuarde el nuevo archivo.
2. Cree el nuevo archivo ejecutable:
chmod +x nginx-with-tls13-compile.shvolver a escribir nginx.service
3.Haga una copia de seguridad de nginx.service.
cat /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service > /srv/nginx_service.txt(puedes elegir el camino que quieras para nginx_service.txt)
4. Crea el archivo para el servicio. nginx: nginx.service
sudo nano nginx.service5. En el archivo el nuevo archivo nginx.service agrega las líneas:
## /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
[Unit]
Description=The NGINX HTTP and reverse proxy server
After=syslog.target network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/run/nginx.pid
ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx
ExecReload=/usr/sbin/nginx -s reload
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target6. Copie el archivo a ‘daemon“.
sudo cp nginx.service /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service7. Una vez copiado el archivo, actualice los permisos del archivo usando el comando:
sudo chmod 644 /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service8. Vuelva a cargar la configuración. systemd para tener en cuenta los cambios usando el comando:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload9. Reiniciar ngnix.
sudo systemctl restart nginxrecompilar OpenSSL / NGINX para TLS 1.3
10. En la misma carpeta donde tienes los archivos nginx-with-tls13-compile.sh y nginx.service, crea un nuevo archivo: openssl-1.1-compile.sh.
sudo nano openssl-1.1-compile.shAñade el guión:
#!/bin/bash
## Compile OpenSSL
OPENSSL=openssl-1.1.1h.tar.gz
DONE=openssl-compile-done
if [ ! -f "${DONE}" ] ;then
wget https://www.openssl.org/source/${OPENSSL}
tar zxvf ${OPENSSL}
cd $(basename $OPENSSL .tar.gz)
./config shared no-idea no-md2 no-mdc2 no-rc5 no-rc4 --prefix=/usr/local/
make
sudo make install
cd ..
touch ${DONE}
fi
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/lib64/
read -n1 -r -p "$(/usr/local/bin/openssl version) - Press any key to continue..." key
source ./nginx-with-tls13-compile.shReemplazar “OPENSSL=openssl-1.1.1h.tar.gz” con la versión que desea instalar y recompilar con NGINX.
11. Haga que el script sea ejecutable:
chmod +x openssl-1.1-compile.sh12. Ejecute el comando:
./openssl-1.1-compile.shEspere a que se complete el proceso de recompilación. OpenSSL & NGINX.
Si podemos ayudarlo o hay cosas que hacer, la sección de comentarios está abierta.
Recompilare OpenSSL 1.1 & Ningin 1.25 para TLS 1.3 (Centos 7)
Qué hay de nuevo
Acerca de Stealth
Apasionado por la tecnología, escribo con gusto en StealthSettings.com desde el año 2006. Tengo una amplia experiencia en sistemas operativos: macOS, Windows y Linux, así como en lenguajes de programación y plataformas de blogs (WordPress) y para tiendas en línea (WooCommerce, Magento, PrestaShop).
Ver todas las publicaciones de StealthTambién te puede interesar...

