Recompilare OpenSSL 1.1 & Ningin 1,25 dla TLS 1.3 (Centos 7)

Recompilare OpenSSL 1.1 & NGINX 1.25 Do TLS 1.3 (CentOS 7), urmând scenariul în care ai deja instalat pe server o versiune mai veche openssl asociată serviciului nginx.
treść
Mai exact, să poți activa OpenSSL 1.1.1t pentru serviciul NGINX, care rulează cu o versiune mai veche. OpenSSL 1.0.2k.
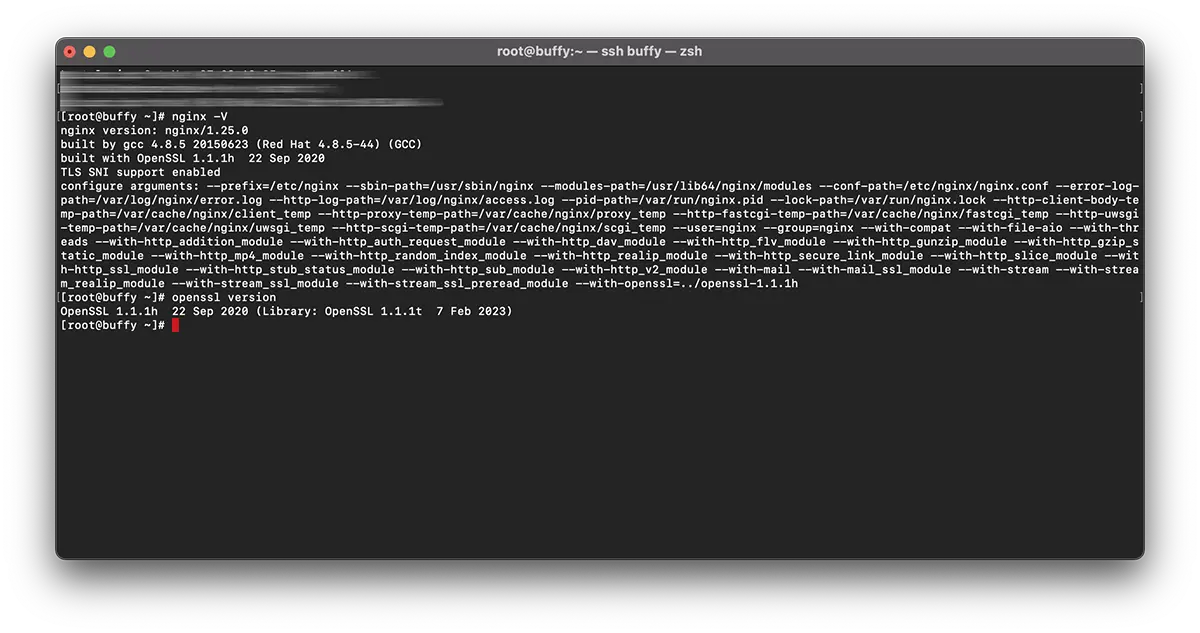
# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.25.0
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
TLS SNI support enabled# openssl version -a
OpenSSL 1.1.1t 7 Feb 2023Asta înseamnă că pe server se află doua versiuni diferite ale OpenSSL. O versiune instalată pe sistem prin “yum” (1.0.2k-fips) și o versiune OpenSSL instalată prin compilare manuală (openssl 1.1.1t).
În mod clasic, majoritatea recomandă reinstalarea ‘OpenSSL‘ la nivel de serever. Asta ar presupune executarea comenzii: yum remove openssl. Numai că aici există o mare problemă. Odată cu dezinstalarea vechii versiuni OpenSSL, może być konieczne odinstalowanie niektórych zależnych aplikacji. Jak na przykład: nginx, MariaDB-server, cerbot, a także wiele innych.
- Jak aktywować TLSV1.3 na NINX. Vestacp / centos lub ubuntu
- Maksymalny okres ważności certyfikatów TLS/SSL w 2023 roku
- Różnice między TLS 1.2 i TLS 1.3 – Prędkość i bezpieczeństwo
Prostszym rozwiązaniem jest rekompilacja openssl 1.1 & nginx 1.25 Do TLS 1.3.
Ponowna kompilacja samouczka OpenSSL 1.1 & NGINX 1.25 Do TLS 1.3 (CentOS 7)
W moim przykładzie rekompilacja służy do nginx/1.25.0 & OpenSSL 1.1.1h korzystając z księgarń OpenSSL 1.1.1t.
Recompilare NGINX.
1. Utwórz plik: nginx-with-tls13-compile.sh
sudo nano nginx-with-tls13-compile.shgdzie dodajesz skrypt:
#!/bin/bash
## nginx
NGINX=nginx-1.25.0.tar.gz
if [ ! -f "${NGINX}" ];then
wget https://nginx.org/download/${NGINX}
fi
ND=$(basename $NGINX .tar.gz)
if [ ! -d "${ND}" ];then
tar zxvf ${NGINX}
fi
cd ${ND}
## pre require package
## yum install gcc pcre-devel zlib-devel
./configure --prefix=/etc/nginx \
--sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx \
--modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules \
--conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf \
--error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log \
--http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \
--pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid \
--lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock \
--http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_temp \
--http-proxy-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp \
--http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp \
--http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp \
--http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp \
--user=nginx \
--group=nginx \
--with-compat \
--with-file-aio \
--with-threads \
--with-http_addition_module \
--with-http_auth_request_module \
--with-http_dav_module \
--with-http_flv_module \
--with-http_gunzip_module \
--with-http_gzip_static_module \
--with-http_mp4_module \
--with-http_random_index_module \
--with-http_realip_module \
--with-http_secure_link_module \
--with-http_slice_module \
--with-http_ssl_module \
--with-http_stub_status_module \
--with-http_sub_module \
--with-http_v2_module \
--with-mail \
--with-mail_ssl_module \
--with-stream \
--with-stream_realip_module \
--with-stream_ssl_module \
--with-stream_ssl_preread_module \
--with-openssl=../$(basename $OPENSSL .tar.gz)
make
sudo make install
nginx -VZapisz nowy plik.
2. Utwórz nowy plik wykonywalny:
chmod +x nginx-with-tls13-compile.shprzepisać nginx.service
3. Zrób kopię zapasową nginx.service.
cat /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service > /srv/nginx_service.txt(możesz wybrać dowolną ścieżkę nginx_service.txt)
4. Utwórz plik dla usługi nginx: nginx.service
sudo nano nginx.service5. W pliku nowy plik nginx.service dodaj linie:
## /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
[Unit]
Description=The NGINX HTTP and reverse proxy server
After=syslog.target network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/run/nginx.pid
ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx
ExecReload=/usr/sbin/nginx -s reload
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target6. Skopiuj plik do ‘daemon“.
sudo cp nginx.service /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service7. Po skopiowaniu pliku zaktualizuj uprawnienia pliku za pomocą polecenia:
sudo chmod 644 /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service8. Załaduj ponownie konfigurację systemd aby uwzględnić zmiany za pomocą polecenia:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload9. Uruchom ponownie ngnix.
sudo systemctl restart nginxRecompilare OpenSSL / NGINX Do TLS 1.3
10. W tym samym folderze, w którym znajdują się pliki nginx-with-tls13-compile.sh I nginx.service, utwórz nowy plik: openssl-1.1-compile.sh.
sudo nano openssl-1.1-compile.shDodaj skrypt:
#!/bin/bash
## Compile OpenSSL
OPENSSL=openssl-1.1.1h.tar.gz
DONE=openssl-compile-done
if [ ! -f "${DONE}" ] ;then
wget https://www.openssl.org/source/${OPENSSL}
tar zxvf ${OPENSSL}
cd $(basename $OPENSSL .tar.gz)
./config shared no-idea no-md2 no-mdc2 no-rc5 no-rc4 --prefix=/usr/local/
make
sudo make install
cd ..
touch ${DONE}
fi
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/lib64/
read -n1 -r -p "$(/usr/local/bin/openssl version) - Press any key to continue..." key
source ./nginx-with-tls13-compile.shZastępować “OPENSSL=openssl-1.1.1h.tar.gz” z wersją, którą chcesz zainstalować i ponownie skompilować za pomocą NGINX.
11. Spraw, aby skrypt był wykonywalny:
chmod +x openssl-1.1-compile.sh12. Uruchom polecenie:
./openssl-1.1-compile.shPoczekaj na zakończenie procesu ponownej kompilacji OpenSSL & NGINX.
Jeśli możemy Ci pomóc lub chcesz coś dodać, sekcja komentarzy jest otwarta.
Recompilare OpenSSL 1.1 & Ningin 1,25 dla TLS 1.3 (Centos 7)
Co nowego
O Stealth
Pasjonat technologii, z przyjemnością piszę na StealthSettings.com od 2006 roku. Mam bogate doświadczenie w systemach operacyjnych: macOS, Windows i Linux, a także w językach programowania i platformach blogowych (WordPress) oraz dla sklepów internetowych (WooCommerce, Magento, PrestaShop).
Zobacz wszystkie posty StealthMoże zainteresują Cię także...

