How do you look and replace a word from a file on Linux

There are many situations where we need to replace a word from the interior of a file. Whether it is a service configuration file, a text file or a file that contains databases, in this tutorial you learn how to look for and replace a word on Linux.
How do you look and replace a word from a file on Linux
What simpler variant if you are a linux operating system user is to use the order “sed“. Order for stream editor.
Let's say as an example we have in a text file (document.txt) the word “abc” that we want to replace with “xyz“. The command line through which we can replace the word will be as follows:
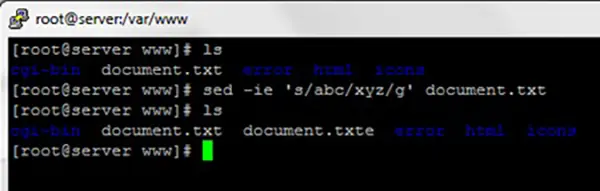
sed -ie 's/abc/xyz/g' document.txtWhen we execute the order, the condition is to be in the folder where the file is located document.txt.
If the order is executed from another location, the full path of the file will be written. For example:
sed -ie 's/abc/xyz/g' /full/path/document.txtWhere “/full/path/” is the folder in which the file is located document.txt.
After executing the order line, the option “-i“ will create one backup file identical to the original one, but to the extension to which the letter will add “e“. In our case the backup document will be document.txte.
- Recompilare OpenSSL 1.1 & Ningin 1.25 for TLS 1.3 (Centos 7)
- How to change mysql root password to Linux (SSH)
-i[SUFFIX], --in-place[=SUFFIX] : edit files in place (makes backup if extension supplied)
-e script, --expression=script : add the script to the commands to be executed.This command of “find & replace” not only valid for files .txt. You can replace words inside any file containing text. Even in files of databases MySQL (.SQL)
Stealth Settings – Find & Replace Inside a Text File (Linux Bash Command Line).
How do you look and replace a word from a file on Linux
What’s New
About Stealth L.P.
Founder and editor Stealth Settings, din 2006 pana in prezent. Experienta pe sistemele de operare Linux (in special CentOS), Mac OS X , Windows XP > Windows 10 si WordPress (CMS).
View all posts by Stealth L.P.You may also be interested in...

