How to recover the password for the user root of a SQL server
Tutorial step by step in which you learn how to recover the password for the user root of a SQL server.
The most important user of a server MySQL is definitely the user “root“. This user has all administrative privileges for databases (MySQL databases).
If you no longer know what is the mysql user's root password, you will need to follow a few simple steps to reset this password.
The tutorial is made for a server MySQL installed on operating system Centos, however, the process is the same for other Linux distributions.
How to recover the password for the user root of a SQL server
To recover the password for the user root of a SQL server, the simplest method is by SSH (Secure Shell).
1. We log with the user “root” to the system on which the MySQL server is. (the system root user, not the MySQL server). Log in directly from the console or remotely by connection ssh (cu putty from Windows systems).
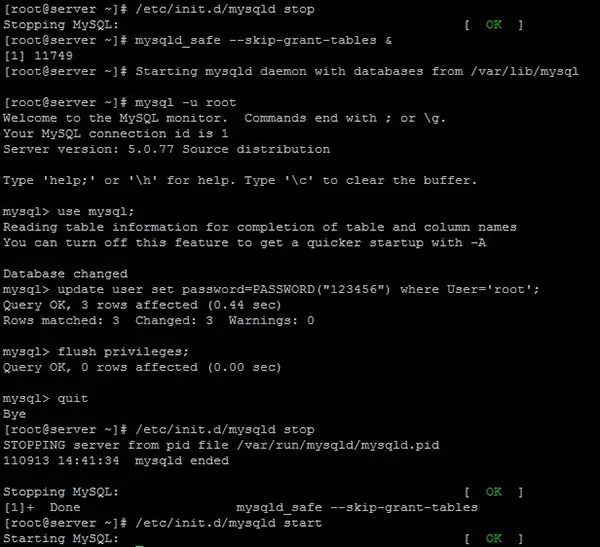
2. We stop the process / mysql server.
service mysqld stopor
/etc/init.d/mysqld stopThe result will be:
Stopping MySQL: [ OK ]3. We start mysql server with option “--skip-grant-tables“. Starting mysql server/daemon process without password.
mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables &The result by the above command line:
[1] 3041
[root@server ~]# Starting mysqld daemon with databases from /var/lib/mysql4. We connect to the MySQL server with the user “root“, using the order:
mysql -u rootThe result of the order:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 1
Server version: 5.0.77 Source distribution
Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the buffer.
mysql>5. We select mysql base and set the new password for the user “root“.
use mysql;
update user set password=PASSWORD("New_Password") where User='root';
flush privileges;
quitRESULTS Following the above orders:
mysql> use mysql;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> update user set password=PASSWORD("123456") where User='root';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 3 Changed: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> quit
Bye
[root@server ~]#6. We stop and restart the service / server MySQL
service mysqld stop
service mysqld startResult:
Starting MySQL: [ OK ]In the picture below is shown everything Password reset process USER SITE “root” of the server MySQL.
Now we can connect to mysql (by phpMyAdmin eg with the user “root”, using the new password set above.
Tutorial tested on Centos 5.6 cu MySQL Ver 14.12 Distrib 5.0.77, for redhat-linux-gnu (i686) using readline 5.1.
How to recover the password for the user root of a SQL server
What’s New
About Stealth L.P.
Founder and editor Stealth Settings, din 2006 pana in prezent. Experienta pe sistemele de operare Linux (in special CentOS), Mac OS X , Windows XP > Windows 10 si WordPress (CMS).
View all posts by Stealth L.P.You may also be interested in...


One thought on “How to recover the password for the user root of a SQL server”