
Clean DNS cache to protect your privacy. (Clean, Enable, Disable DNS cache – Windows XP, Vista & Windows 7)
Clean DNS cache to protect your privacy. (Clean, Enable, Disable DNS cache – Windows XP, Vista & Windows 7)

DNS Cache (Caching name servers), is a process by which it is stored a query DNS of an application (Internet Browser, client FTP, Yahoo! Messenger, etc …). Basically, this process helps the servers that hold the domain names, to store for a period of time (determined by the server configuration) query data on the end user's computer. In this way, a higher response speed of the web server or the server that holds data about an application is obtained and a communication bridge is created between the PC and the server.
A number of applications use the DNS cache while the application is running to check updatethe updates or even license validity.
If you are curious to see which servers have DNS caches on your PC, open (with administrator privileges) a Command Prompt (Ctrl+Win > cmd > Enter) if you typed:
ipconfig /displaydns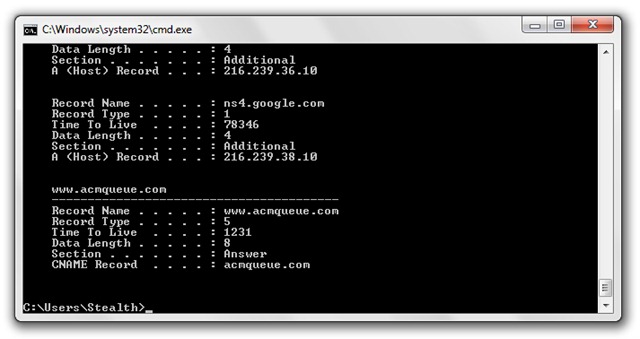
In order to clean DNS cache, type in CMD :
ipconfig /flushdnsIn CMD you should receive the message:
Windows IP Configuration
Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache.
Enable and disable DNS cache (DNS Client service) :
net stop dnscache
net start dnscacheDNS Cache Reference (Recursive and caching name server) (Wikipedia).
Stealth Settings – CLEAN, ENABLE & DISABLE DNS CACHE.
Clean DNS cache to protect your privacy. (Clean, Enable, Disable DNS cache – Windows XP, Vista & Windows 7)
What’s New
About Stealth L.P.
Founder and editor Stealth Settings, din 2006 pana in prezent. Experienta pe sistemele de operare Linux (in special CentOS), Mac OS X , Windows XP > Windows 10 si WordPress (CMS).
View all posts by Stealth L.P.You may also be interested in...


11 thoughts on “Clean DNS cache to protect your privacy. (Clean, Enable, Disable DNS cache – Windows XP, Vista & Windows 7)”