In short, “of” (Disk Usage) Este order Linux / Unix through which we can Check the busy volume (use information) on hard disk of leaflets and FILES.
A very useful order especially when we are limited by the space of a hard drive – or SSD – and we want to find out quickly who they are files and / or Folders the most “BULKY”. of course command “of” It can be used in a variety of syntaxs that will return the desired use information.
Syntax of the order line “of” It is very simple and very flexible, as are all Linux commands.
In the order documentation “of”, the following options are presented to us:
[root@server]# you –help
Usage: you [option]… [FILE]…
Gold: [option]… –files0-from=F
Summarize disk usage of each FILE, recursively for directories.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-a, –all write counts for all files, not just directories
–apparent-size print apparent sizes, rather than disk usage; although the apparent size is usually smaller, it may be larger due to holes in (`sparse’) files, internal fragmentation, indirect blocks, and the like
-B, –block-size=SIZE use SIZE-byte blocks
-b, –bytes equivalent to `–apparent-size –block-size=1′
-c, –total produce a grand total
-D, –dereference-args dereference only symlinks that are listed on the command line
–files0-from=F summarize disk usage of the NUL-terminated file names specified in file F;
If F is – then read names from standard input
-H equivalent to –dereference-args (-D)
-h, –human-readable print sizes in human readable format (e.g., 1K 234M 2G)
–si like -h, but use powers of 1000 not 1024
-k like –block-size=1K
-l, –count-links count sizes many times if hard linked
-m like –block-size=1M
-L, –dereference dereference all symbolic links
-P, –no-dereference don’t follow any symbolic links (this is the default)
-0, –null end each output line with 0 byte rather than newline
-S, –separate-dirs do not include size of subdirectories
-s, –summarize display only a total for each argument
-x, –one-file-system skip directories on different file systems
-X, –exclude-from=FILE exclude files that match any pattern in FILE
–exclude=PATTERN exclude files that match PATTERN
–max-depth=N print the total for a directory (or file, with –all) only if it is N or fewer levels below the command line argument; –max-depth=0 is the same as
–summarize
–time show time of the last modification of any file in the directory, or any of its subdirectories
–time=WORD show time as WORD instead of modification time: atime, access, use, ctime or status
–time-style=STYLE show times using style STYLE: full-iso, long-iso, iso, +FORMAT
FORMAT is interpreted like `date’
–help display this help and exit
–version output version information and exit
Display values are in units of the first available SIZE from –block-size, and the DU_BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE and BLOCKSIZE environment variables.
Otherwise, units default to 1024 bytes (or 512 if POSIXLY_CORRECT is set).
SIZE may be (or may be an integer optionally followed by) one of following: KB 1000, K 1024, MB 1000*1000, M 1024*1024, and so on for G, T, P, E, Z, Y.
All the above options can be combined in order lines that will display exact reports about the targeted files and directors. For example, if we want to see the individual volume of folders and files in a certain location (/lime, in our example), the command line will:
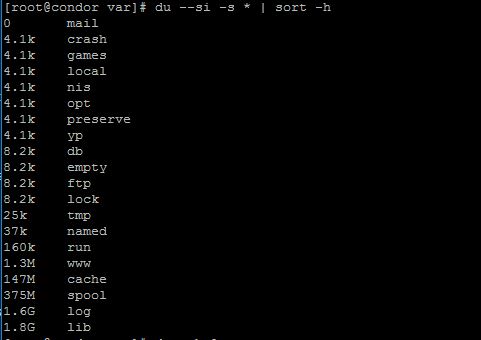
du --si -s * | sort -hThis means displaying the individual volume occupied by the folders and files below /lime, sorted down.
“sort -h” – sort and display the result in “Human Readable Format“.Bytes, Kilobytes, Megabytes, Gigabytes.
“–and” – has some of the same function as “-h”, but uses 1000 instead of 1024.
“-s” – He displays the total for the parent director, without detailing the folders and files under him.
du (Disk Usage) Command in Linux
What’s New
About Stealth
Passionate about technology, I write with pleasure on stealthsetts.com starting with 2006. I have a rich experience in operating systems: Macos, Windows and Linux, but also in programming languages and blogging platforms (WordPress) and for online stores (WooCommerce, Magento, Presashop).
View all posts by StealthYou may also be interested in...