Find your files faster using Indexing Service

Ca utilizator XP, de fiecare data cand aveam nevoie de anumite fisiere stocate prin cine stie ce colturi intunecate ale hard-diskurilor, aveam, implicit, o zi proasta. Si asta pentru ca search-ul integrat in sistem mi-a pus de nenumarate ori rabdarea la incercare, prin modul lent de a afisa rezultatele si, mai ales, pentru ca tipurile de cautari pe care acesta le efectueaza sunt limitate.
Pana am descoperit Indexing Service (Serviciul de Indexare) al Microsoftului, o utilitate care poate efectua cautari de sute de ori mai rapid decat search-ul obisnuit, prin folosirea unui limbaj specific. Indexing Service (prescurtat IS) indexeaza fisierele de pe hard-diskul dvs. (formand asa-zisele cataloage), la o cautare ulterioara, acesta interogand indexul, in loc sa scotoceasca fiecare folder in parte.
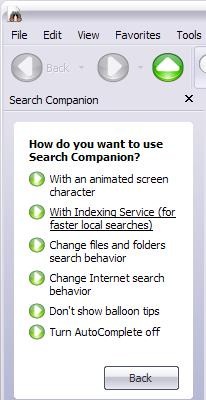
IS nu este activat default. Pentru a-l activa mergeti la Start->Search. In fereastra deschisa, dati click pe Change Preferences si selectati With Indexing Service. Daca optiunea With Indexing Service nu este disponibila, in schimb aveti optiunea Without Indexin Service, inseamna ca IS este deja activat.
IS nu va fi disponibil imediat dupa activare. In primul rand, acesta trebuie sa creeze indexul, care dureaza in functie de numarul fisierelor de pe hard-disk si in functie de viteza procesorului. De aceea, cand activati IS, este recomandat sa lasati PC-ul in repaus cateva ore, pentru ca acesta sa poata efectua indexarea.
Limbajul specific al IS foloseste tag-uri (etichete) pentru definirea criteriilor de cautare. Interogarile sunt facute sub forma {prop name=property name} interogare {/prop}, property name insemnand numele proprietatii respective, cum ar fi cele listate in tabelele urmatoare, iar interogarea reprezinta textul pe care il cautati. De exemplu, in cazul in care doriti sa cautati fisiere care au fost reeditate recent de un anumit autor, cum ar fi Stealth Settings, veti face interogarea in urmatorul fel:
{prop name = DocLastAuthor} Stealth Settings {/prop}
| Property | Description |
| Access | The last time the document was accessed. |
| All | All available properties. Works with text queries but not numeric queries. |
| AllocSize | The total disk space allocated to the document. |
| Contents | The contents of the document. |
| Created | The time the document was created. |
| Directory | The full directory path in which the document is contained. |
| DocAppName | The name of the application in which the document was created. |
| DocAuthor | The author of the document. |
| DocByteCount | DocByteCount The number of bytes in the document. |
| DocCategory | The type of document. |
| DocCharCount | The number of characters in the document. |
| DocComments | Comments made about the document. |
| DocCompany | The name of the company for which the document was written. |
| DocCreatedTime | The time spent editing the document. |
| DocHiddenCount | The number of hidden slides in a PowerPoint document. |
| DocKeyWords | The keywords in the document. |
| DocLastAuthor | The name of the person who last edited the document. |
| DocLastPrinted | The time the document was most recently printed. |
| DocLineCount | The number of lines contained in the document. |
| DocLastSavedTm | The time the document was last saved. |
| DocManager | The name of the manager of the document’s author. |
| DocNoteCount | The number of pages with notes in a PowerPoint document. |
| DocPageCount | The number of pages in the document. |
| DocParaCount | The number of paragraphs in the document. |
| DocPartTitles | The names of document parts, such as spreadsheet names in an Excel document or slide titles in a PowerPoint slide show. |
| DocRevNumber | The current version number of the document. |
| DocSlideCount | The number of slides in a PowerPoint document. |
| DocTemplate | The name of the document’s template. |
| DocTitle | The title of the document. |
| DocWordCount | The number of words in the document. |
| FileName | The fi lename of the document.The fi lename of the document. |
| Path | The path to the document, including the document fi lename. |
| ShortFileName | The 8.3-format name of the document. |
| Size | The size of the document, in bytes. |
| Write | The date and time the document was last modifi ed. |
Cautarile pot fi efectuate si in functie de frazele continute de fisiere, folosind interogarea {phrase} fraza {/phrase}:
{phrase} Tips and hacks for Windows XP {/phrase}
Pentru a cauta texte, puteti folosi tipul de interogare descris mai sus (phrase) sau interogarea freetext. Diferenta dintre aceste doua consta in faptul ca phrase face cautarea dupa ordinea cuvintelor, adica rezultatele vor include numai fisierele care contin fraza exacta, iar freetext face interogarile dupa fiecare cuvant din fraza, rezultatele fiind mai numeroase, deoarece vor include toate fisierele care contin cel putin un cuvant din fraza respectiva.
IS va ofera posibilitatea sa faceti cautarile si in functie de timpurile si modurile verbelor, prin folosirea de metacaractere cum ar fi dublu asterix (**). Astfel o cautare de genul {prop name=Contents} write** {/prop} va avea ca rezultat toate fisierele care contin formele alternative ale verbului “to write” (a scrie), cum ar fi write, wrote, written.
Concluzie: Recomand folosirea Indexing Service doar de catre utilizatorii care au cunostinte avansate de folosire a sistemului de operare Windows XP. Pentru incepatori este mai simplu de utilizat Search-ul integrat in sistem.
Find your files faster using Indexing Service
What’s New
About Stealth
Pasionat de tehnologie, scriu cu plăcere pe StealthSettings.com începând cu anul 2006. Am o bogată experiență în sistemele de operare: macOS, Windows și Linux, dar și în limbaje de programare și platforme de blogging (WordPress) și pentru magazine online (WooCommerce, Magento, PrestaShop).
View all posts by StealthTe-ar putea interesa și...


2 thoughts on “Find your files faster using Indexing Service”