Find your files faster using Indexing Service

As a user XP, every time I needed some FILES Stored by who knows what dark corners of the hard disk, I had, by default, a bad day. And that's because Search integrated in system has put my patience to the test, through slow way of displaying results and, above all, because the types of searches they perform are limited.
Until I discovered Indexing Service (Indexing service) al where Microsoft, a utility that can perform Search for hundreds of times faster than the usual search by using a Specific language. Indexing Service (shortened IS) indexes files on your hard disk (forming so-called catalogs), at a subsequent search, it interrogating the index, instead of scoring each folder separately.
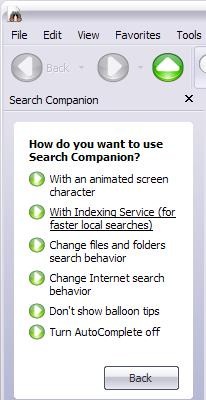
Is not activated default. To activate it go to Start->Search. In the open window, click on Change Preferences and select With Indexing Service. If the WITH Indexing Service option is not available, instead you have the option Without Indexin Service, means that IS is already activated.
IS will not be available immediately after activation. First of all, it must create the index, which lasts according to the number of files from the hard disk and according to the speed of the processor. Therefore, when activating IS, it is advisable to leave the PC at rest for several hours, so that it can carry out the index.
The specific language of IS is using tag-uri (Tags) to define search criteria. Interrogations are made in the form {prop name=property name} interogare {/prop}, Property Name meaning the name of the respective property, such as those listed in the following tables, and the query represents the text you are looking for. For example, if you want to look for files that have been recently reissued by a certain author, such as Stealth Settings, you will make the query as follows:
{prop name = DocLastAuthor} Stealth Settings {/prop}
| Property | Description |
| Access | The last time the document was accessed. |
| All | All available properties. Works with text queries but not numeric queries. |
| AllocSize | The total disk space allocated to the document. |
| Contents | The contents of the document. |
| Created | The time the document was created. |
| Directory | The full directory path in which the document is contained. |
| DocAppName | The name of the application in which the document was created. |
| Docauthor | The author of the document. |
| DocByteCount | DocByteCount The number of bytes in the document. |
| DocCategory | The type of document. |
| DocCharCount | The number of characters in the document. |
| DocComments | Comments made about the document. |
| DocCompany | The name of the company for which the document was written. |
| DocCreatedTime | The time spent editing the document. |
| Dochissercount | The number of hidden slides in a PowerPoint document. |
| DocKeyWords | The keywords in the document. |
| DocLastAuthor | The name of the person who last edited the document. |
| DocLastPrinted | The time the document was most recently printed. |
| DocLineCount | The number of lines contained in the document. |
| DocLastSavedTm | The time the document was last saved. |
| DocManager | The name of the manager of the document’s author. |
| DocNoteCount | The number of pages with notes in a PowerPoint document. |
| DocPageCount | The number of pages in the document. |
| DocParaCount | The number of paragraphs in the document. |
| DocPartTitles | The names of document parts, such as spreadsheet names in an Excel document or slide titles in a PowerPoint slide show. |
| DocRevNumber | The current version number of the document. |
| Docslidecount | The number of slides in a PowerPoint document. |
| Doctor | The name of the document’s template. |
| DocTitle | The title of the document. |
| DocWordCount | The number of words in the document. |
| FileName | The fi lename of the document.The fi lename of the document. |
| Path | The path to the document, including the document fi lename. |
| ShortFileName | The 8.3-format name of the document. |
| Size | The size of the document, in bytes. |
| Write | The date and time the document was last modifi ed. |
Searches can be performed and Depending on the phrases contained in files, using query {phrase} FRAZA {/phrase}:
{phrase} Tips and hacks for Windows XP {/phrase}
To look for texts, you can use the type of query described above (phrase) or query freetext. The difference between these two consists in the fact that Phrase makes Search for the order of words, that is, the results will only include files containing the exact phrase, and freetext does interrogations after every word in the phrase, the results being more numerous because they will include all files containing at least one word in that phrase.
Is offers you the opportunity to do the searches and Depending on the times and modes of verbs, by using metacaractere such as double asterix (**). Thus a search like {prop name=Contents} write** {/prop} It will result in all files that contain the alternative forms of the verb "to write" (write), such as Write, Wrote, Written.
Conclusion: I recommend using Indexing Service only by Users who have advanced knowledge of using Windows XP operating system. For beginners it is easier to use the integrated search in the system.
Find your files faster using Indexing Service
What’s New
About Stealth
Passionate about technology, I write with pleasure on stealthsetts.com starting with 2006. I have a rich experience in operating systems: Macos, Windows and Linux, but also in programming languages and blogging platforms (WordPress) and for online stores (WooCommerce, Magento, Presashop).
View all posts by StealthYou may also be interested in...


2 thoughts on “Find your files faster using Indexing Service”